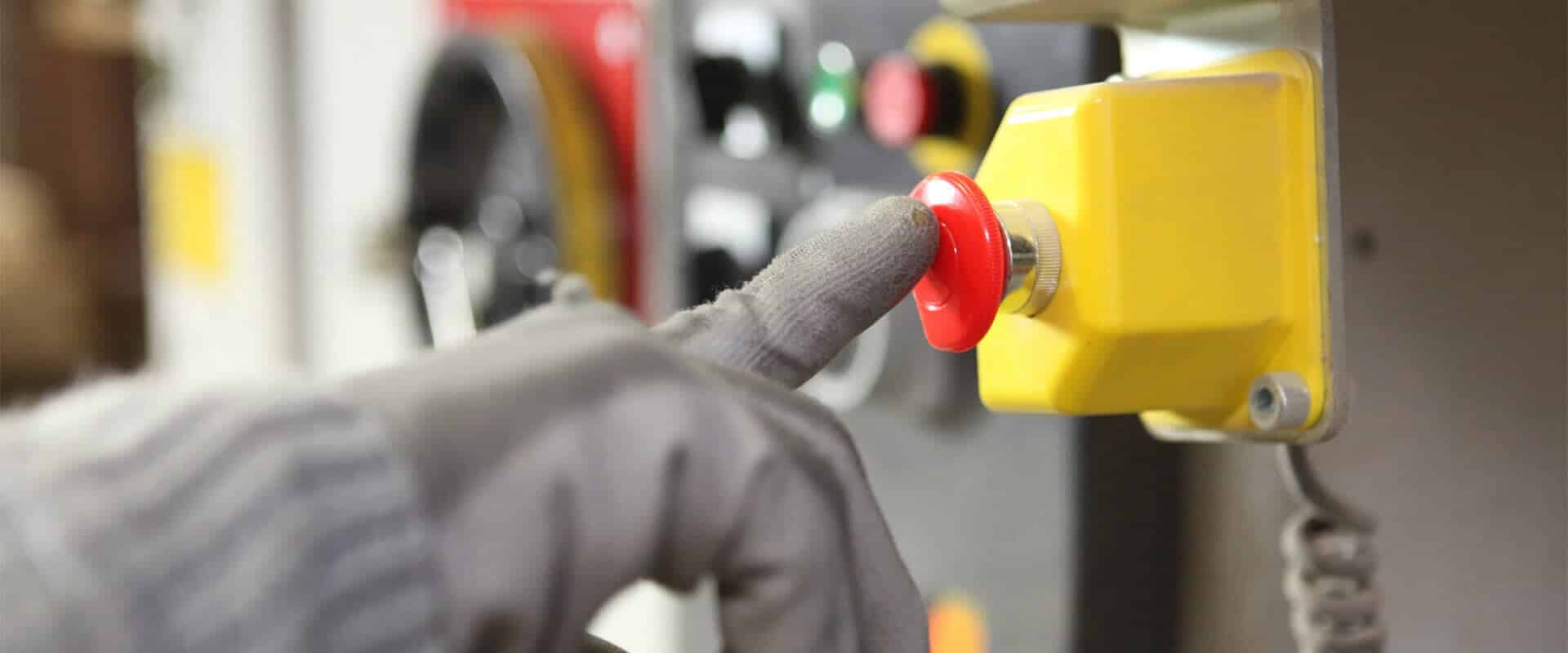
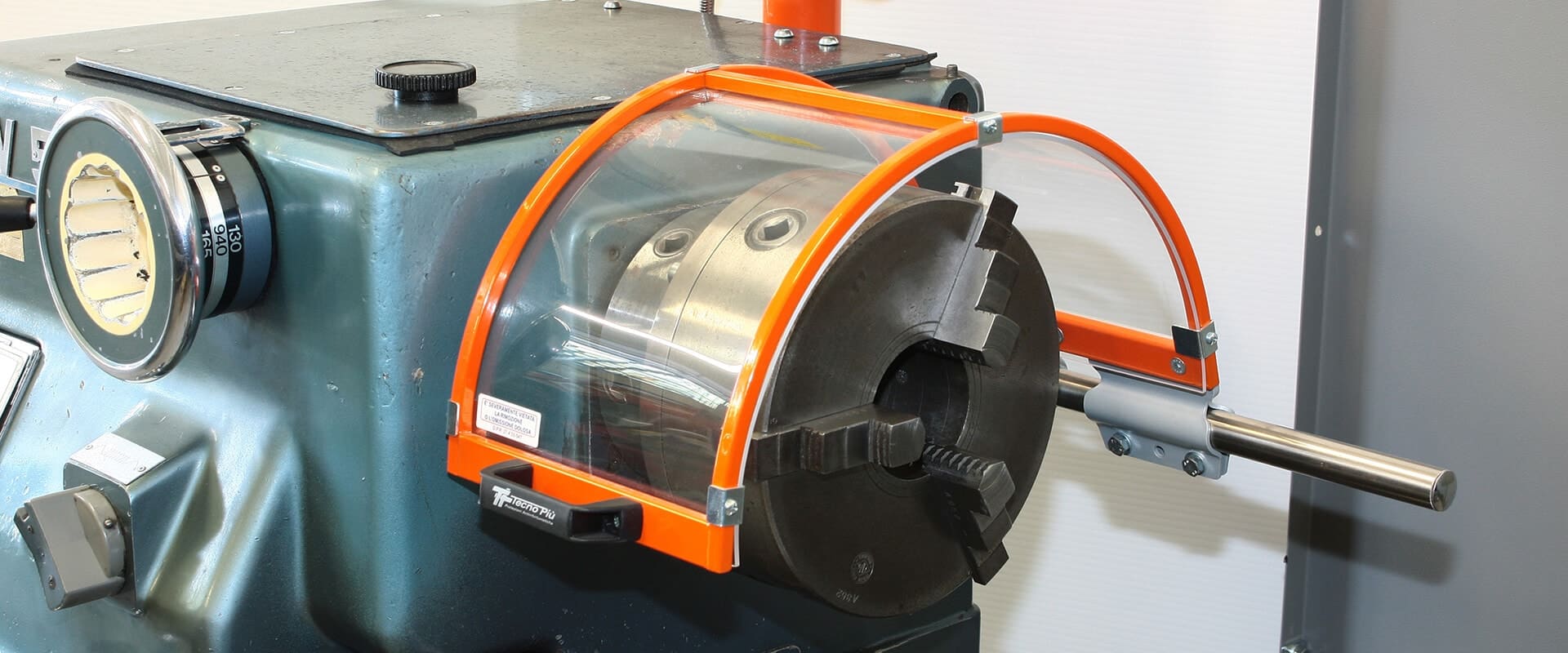
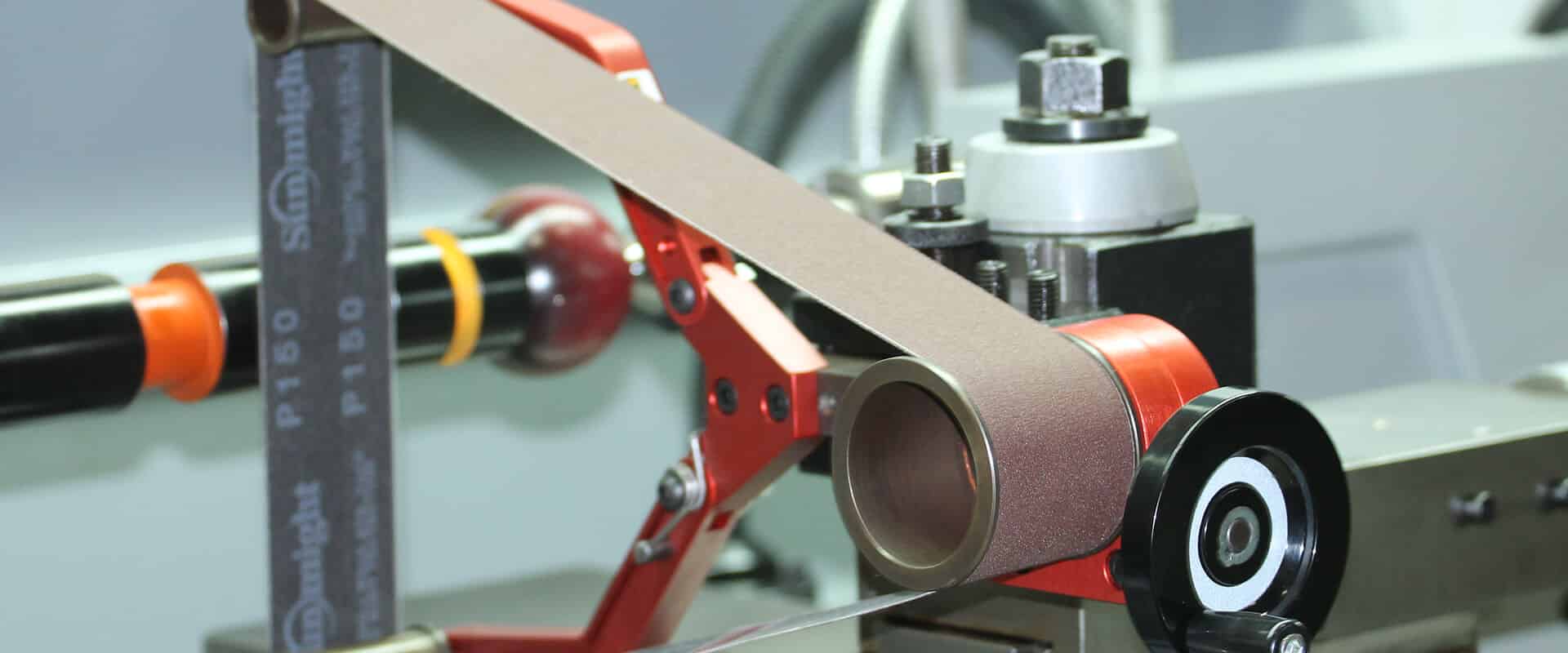
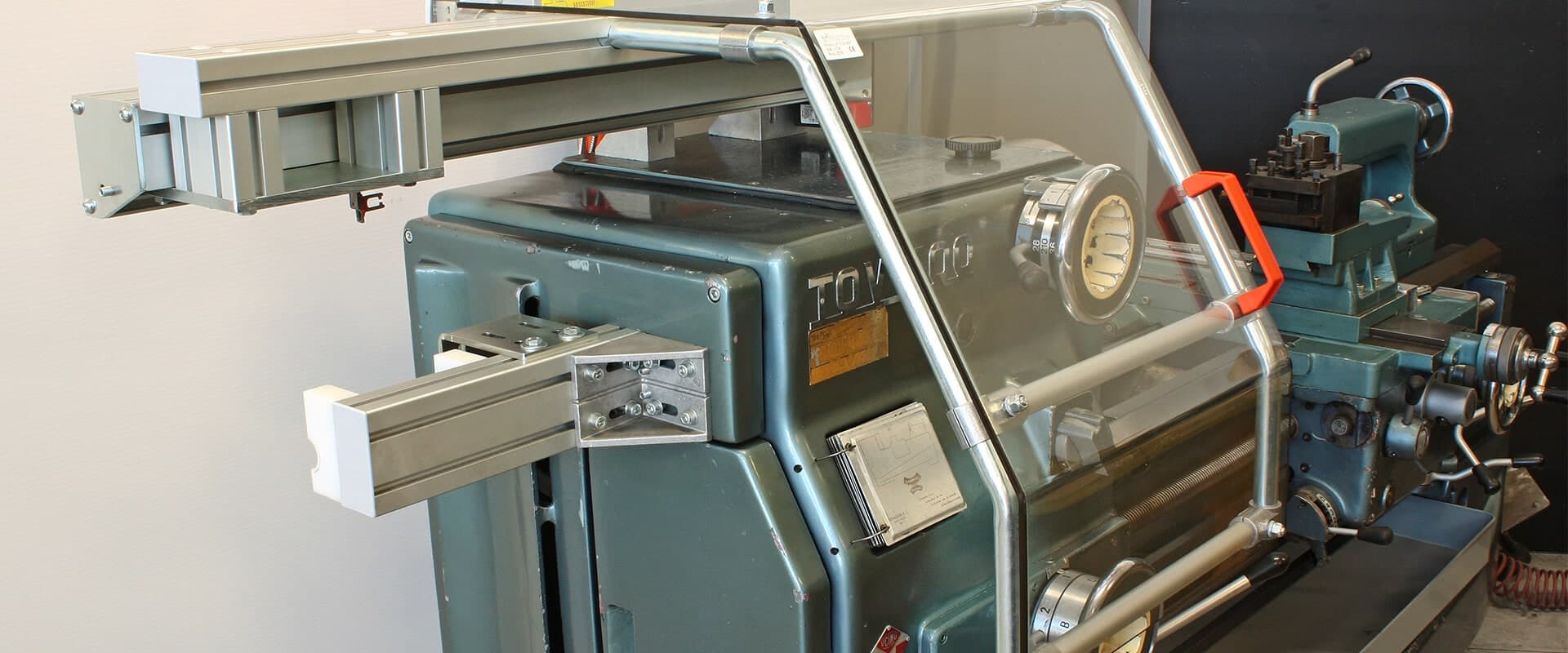
Workplace safety is at the core of PRISMONT’s values. This is why we recommend our clients implement interlocked protection rather than their unlocked versions. Safe and effective, most of the machine tooling safety guards offered by PRISMONT come with an interlocking system.
Interlocking is a safety mechanism that prevents accidents and ensures safe working conditions. Interlocks for machine tool guards prevent the machine from operating if the guards are not correctly in place. According to ISO 14119, an interlocking device is a: "mechanical, electrical or other type of device, the purpose of which is to prevent the operation of hazardous machine functions under specified conditions (generally as long as a guard is not closed).".
An interlocked guard must meet three criteria :
The definition of this type of guard may slightly differ between various safety standards, but the logic remains exactly the same. To be effective, an interlocking device must not be easily bypassed or disabled.
Interlocked safety guards are safer than non-interlocked guards. Interlocked guards are equipped with locking systems that prevent the operator from opening the guard while the machine is running. This way, the operator cannot access moving parts, significantly reducing the risk of injuries. On the other hand, non-interlocked guards can be easily bypassed by the operator, leading to serious injuries or property damage.
Some machines have parts that continue to move after the machine is stopped. For example, a large saw blade or one spinning at very high speed may continue to spin for several seconds after the machine is stopped. In such a case, an interlocked guard is essential to prevent access to the blade until it is completely stopped.
Interlocking is a crucial element of machine tooling safeguarding and ensures that operations only proceed under safe conditions. This protects operators and ensures proper functioning of the equipment while adhering to safety standards. Therefore, it is highly recommended to install interlocked protective equipment on machines for safe and efficient use.
An interlocking system on a machine tool uses various safety components to ensure the machine only operates when all safety conditions are met. Here are those components and their roles:
A physical barrier preventing access to dangerous parts of the machine during operation. The operator must close this door to prepare the machine.
Devices installed on the safety door and other dangerous points to detect their status (open/closed). Sensors send signals to the programmable logic controller (PLC).
The PLC receives signals from the sensors and makes decisions based on programmed logic. It monitors sensor signals and verifies that all safety conditions are met (door closed, no obstacles, protective devices in place). If a safety condition changes (e.g., door opens or emergency button is pressed), the PLC immediately cuts power to critical components of the machine, stopping it immediately.
Electromechanical devices controlling the power to the machine's components (motors, spindles, etc.). Once safety conditions are validated, the PLC activates these relays and contactors.
Allow immediate stopping of the machine in case of danger.
After an interruption, the operator must correct the safety condition (e.g., close the safety door), reset the system via the PLC, and then restart the machine. The PLC rechecks all safety conditions before allowing the restart to ensure maximum safety.
Several types of interlocking are used to ensure the safety of operators and machine tools. Here are a few:
Uses physical locks and latches: Uses latches, locks, or bars to block or allow the operation of the machine based on the guard's position. For example, a key inserted in a lock allows the machine to operate. The guard can only be opened if the key is removed, stopping the machine.
Limit switch : Detect the position of the guard and control the machine’s electrical circuits. If the guard is open, the circuit is interrupted, stopping the machine.
Combines mechanical and electrical elements to offer a robust and reliable solution. They often use key switches that require capturing a key when the guard is closed. The machine can only start if the key is in place.
Electromechanical Key Switch: Uses a solenoid with a key retention system to lock the guard until the machine is in a safe state. These systems can be used alone or in combination to maximize safety.
Advanced electronic controls: Uses systems like RFID to monitor and manage the position and status of the guard, offering high security and the ability to perform specific configurations. Sensors and electronic controllers monitor and manage the machine.
There are many other types of interlocking systems. To choose the right one, it is necessary to consider the type of machine, its use, its guard, and the applicable safety laws and standards.
Our sales and design team can work with you to determine the appropriate type of stop for your application, taking into account factors such as the application and type of machine, your budget, and applicable laws and standards. Contact us today to start creating a safer workplace.
References
CNESST
La prévention des accidents liés aux pièces en mouvement
GUIDE EXPLICATIF DES EXIGENCES RÉGLEMENTAIRES À L’INTENTION DES MILIEUX DE TRAVAIL
Réglement sur la santé et la sécurité du travail
Amélioration de la sécurité des machines par l’utilisation des dispositifs de protection
IRSST
Les types de dispositifs d’interverrouillage
Intervention prévention